Psoriasis
What is psoriasis?


Psoriasis is a common and often lifelong (chronic), non-contagious disorder of the skin, usually with a genetic component.
It occurs when inflammatory chemicals produced by specialised white blood cells called lymphocytes trigger the proliferation and quick turnover of skin cells.
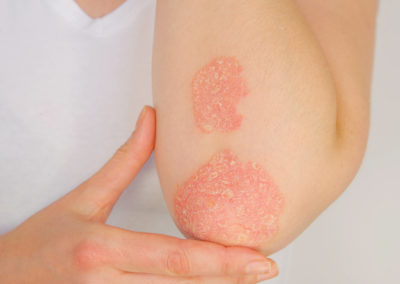
This commonly results in multiple, red, flaky plaques.
The scalp is one of the commonest areas to be affected and often the first site affected.
Plaques tend to be restricted to hair‐bearing areas, extending a short distance beyond the hairline.
The thick plaques of psoriasis are often itchy, tend to flare for weeks or months then go into remission and crop up again later.
Psoriasis typically has two peaks of incidence, the first occurring between 16-22 years and the second between 57 and 62 years of age.
At Aurora Dermatology one of our signature specialties is providing psoriasis injections and biological treatments for psoriasis.
What are the symptoms of psoriasis?
This skin disorder can appear quite differently from individual to individual but common symptoms include:
- Raised and red/silvery flaky plaques
- A small scaling spot (commonly seen in children) right through to major eruptions that cover large areas of the body
- Many patients have shedding of the skin
- Dry cracked skin that may cause burning, soreness, itching, or bleeding
- Psoriasis of the nails can make the nails look thick, pitted and ridged and is often accompanied by swelling in the fingers (psoriatic arthritis)
- This type of arthritic pain can also sometimes impact the fingers, toes, wrists, knees, lower back or ankles
- Pain, stiffness, or both may accompany joint swelling
What are the different types of psoriasis?
It causes dry, raised, red lesions, covered by silvery plaques that usually appear on elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp.
It can cover the entire body and may cause a peeling rash that can cause intense burning, shivering, fluid retention and needs urgent treatment.
What are the causes of psoriasis?
Common factors that can increae your risk include:
- A family history of psoriasis
- Excess coffee and alchohol
- Streptococcal Infection
- Excess sunshine
- Extreme cold and dry weather conditions
- Skin injury such as a srape or cut
- Stress
- Physical Trauma
Drugs such as
- Lithium
- NSAIDS
- Synthetic anti-malarials
- Beta blockers
- ACE Inhibitors
- TNFa inhibitors
- Withdrawal of oral corticosteroids.
Certain c-morbidities
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Depression
- Liver Disease
- Heart Disease
- High Blood Pressure
What are the treatments for psoriasis?
Treatment of psoriasis will depend on the type and severity of the condition.
The main options include medications, phototherapy, and home lifestyle remedies.
Biologic therapies are one of Aurora’s signature treatments for severe psoriasis and have revolutionised the treatment of this disabling condition by targeting the specific parts of the immune system.
However, because these treatments are expensive the government will only subsidise the cost of treatment where the disease is particularly severe or all other options have been exhausted. Check with your dermatologist or GP.
Other effective treatments for psoriasis include:
- Anti-itch agents and hydrocortisone cream (mild psoriasis)
- Topical corticosteroids, cortisone creams/ointments/shampoo
- Vitamin D analogue Daivobet creams/ointments /foam
- Dithranol
- Coal Tar
- Topical Retinoids
- Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus
- Phototherapy, narrow-band UVB Phototherapy with ultraviolet light can reduce irritation and
slow immune activity, although some patients such as those with lupus are not suitable. Click here to learn more about Phototherapy. - Biologic treatment
- Methotrexate
- Psoriasis injections
- Ciclosporin
- Acitretin
- Apremilast
Natural/home remedies do not cure psoriasis, but can alleviate symptoms.
These include frequently moisturising the skin, eating a healthy diet with lots of Omega 3s, stress reduction, and avoiding hot and frequent showers.
To book a consultation with a dermatologist please call us on
02 9423 0033 or email info@auroradermatology.com.au
Sources
– Psoriasis: Symptoms, types, and treatment – Medical News Today
– Study links psoriasis with blood vessel inflammation
– Everything you need to know about Psoriasis – Healthline
– Psoriatic arthritis – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic
– Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes Treatment, Plaque Psoriasis – Cleveland Clinic
– What To Know About Kim Kardashian’s Skin Disorder Psoriasis & How She Copes